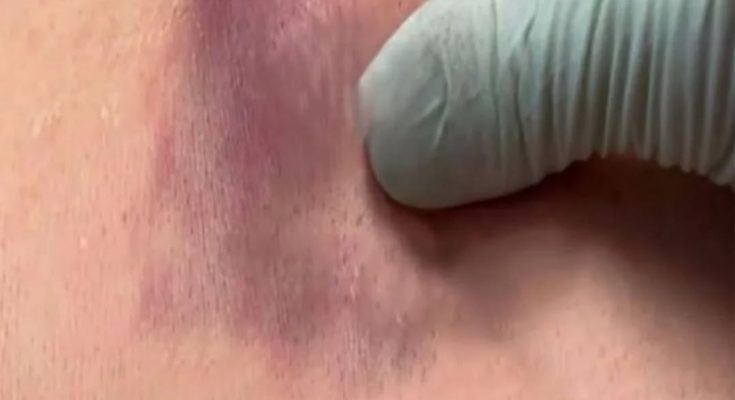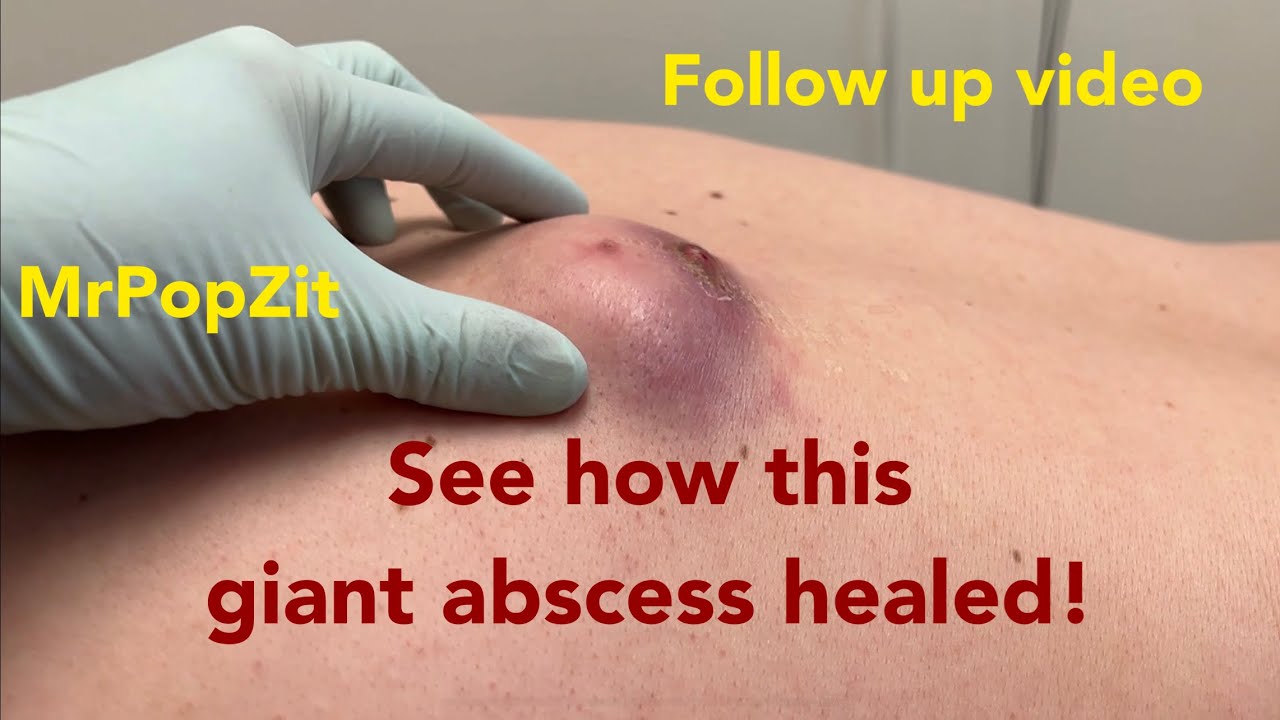
Abscess
What is an abscess?
An abscess is a pocket of . Abscesses can form almost anywhere in or on your body. When you get an infection, your body’s kicks into action to try to fight it. White blood cells travel to the infected area and build up within the damaged tissue. This buildup leads to inflammation, which causes a pocket to form. The pocket fills with pus, creating an abscess. Pus is made up of living and dead white blood cells, germs, fluid and dead tissue.
What are the different types of abscesses?
There are many different kinds of abscesses. Abscesses can develop on your skin, in your mouth or around an internal organ.
Skin abscesses
Skin abscesses (cutaneous abscesses) develop under your skin. They’re common and typically easy to treat. Types of skin abscesses include:
- Armpit abscess: An armpit abscess can occur when pus collects in your armpit. One common cause of armpit abscesses is a condition called Hidradenitis suppurativa causes red, tender bumps in the skin of your armpits that can turn into abscesses over time.
- Breast abscess: is a pocket of pus in your breast. Untreated breast infections can lead to breast abscesses. Breast abscesses often occur in people who are
- Anorectal abscess: An anorectal abscess is an abscess located under the skin around your anus or rectum. A perianal abscess is a type of anorectal abscess that affects the skin around your anus. A is an abscess in the skin of the crease of your buttocks.
Abscesses in your mouth
Abscesses in your can affect your teeth, gums and throat. (dental abscess) is an abscess that forms around a tooth. There are various types of tooth abscesses:
- Gingival abscess: Another name for a gingival abscess is a gum abscess. This type of abscess develops in your It doesn’t usually affect your teeth.
- Periapical abscess: A is an infection that forms at the tip of the root of your tooth. This type of abscess can occur due to
Other abscesses in your mouth may include:
- Tonsil abscess: A tonsillar abscess is a pocket of pus behind one of your. Tonsillar abscesses are most common in adolescents and young adults.
- Peritonsillar abscess: Another name for a is a quinsy. A quinsy is a buildup of pus between your tonsils and the wall of your throat.
- Retropharyngeal abscess: A is an abscess in the back of your . This type of abscess forms when lymph nodes in the back of your throat become infected.
Internal abscesses
Internal abscesses occur much less frequently than external ones, but can develop on your , brain and other organs. Internal abscesses are usually harder to diagnose and treat.
- An abdominal abscess is a buildup of pus inside your belly (abdomen). It may be located inside or near your kidneys, or other organs.
- Spinal cord abscess: A spinal cord abscess is a buildup of pus in and around your spinal cord. An infection on your usually causes a spinal cord abscess.
- A brain abscess is a rare buildup of pus in your brain. An abscess may form in your brain when bacteria from an infection elsewhere in your head or bloodstream or from a wound enter your brain.
Symptoms and Causes
What does an abscess look like?
An abscess under your skin is easy to see. It may appear red, raised and swollen. The skin over the center of the abscess may be thin. It may look yellow or white because there’s pus underneath the surface of your skin. The abscess may feel tender and warm to the touch. Other symptoms of a skin abscess include pain,
An abscess in your mouth may cause a severe. A gum abscess looks like swelling on your gums. Sometimes your jaw, floor of your mouth or cheeks may swell as well. Other symptoms of mouth abscesses include:
- Fever.
- Difficulty opening your mouth.
For deeper skin abscesses or those inside your body, symptoms aren’t as obvious. Some symptoms relate to the part of your body that’s affected. You may experience:
- Pain and tenderness.
- Fever.
- Chills.
- Loss of appetite.
How does an abscess form?
Bacterial infections usually cause abscesses. A bacteria called Staphylococcus causes most abscesses. When bacteria enter your body, your immune system sends to go fight the infection. This process causes , and the tissue nearby dies. When this happens, a pocket forms and fills with pus, creating an abscess.
Rarely, viruses, parasites and fungi can cause abscesses.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is an abscess diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider can diagnose a skin abscess during a They’ll look at the abscess and ask about your symptoms. They may collect a sample of the pus from your abscess for testing. With the sample, your healthcare provider can identify the type of bacteria causing the abscess. This can help them decide on the best course of treatment.
Deeper abscesses, including internal abscesses, are harder to diagnose since you can’t see them. Your healthcare provider may need to order imaging tests. These tests may include:
- An ultrasound is a safe medical imaging test that uses sound waves to create a real-time video of your internal organs.
- A CT scan uses X-rays and computers to create images of a cross-section of your body.
- An MRI uses a large magnet, radio waves and a computer to create clear images of your organs and body structures.
Management and Treatment
How is an abscess treated?
A very small abscess or one close to the surface of your skin may resolve by itself. You may be able to get rid of an abscess by applying a warm compress to the area. It may drain naturally, but you shouldn’t attempt to drain or burst an abscess at home. If you try to squeeze the pus out of an abscess yourself, it can easily spread the bacteria to other areas of your skin.
Your healthcare provider may prescribe an But treatment for an abscess may also require surgical drainage. First, your healthcare provider will apply a local anesthetic to the area around the abscess. With local , you’ll stay awake but the area will be numb.
Your healthcare provider will make a tiny cut (incision) in the abscess. They’ll allow the abscess to drain and remove any remaining pus, dead tissue and debris. They’ll leave the abscess open to allow any remaining pus to drain. (For larger abscesses, they may pack the open abscess with gauze.) Then, they’ll apply a clean, dry bandage to the area. The incision will heal on its own. You may have a scar at the incision site. A scar can tell you your abscess is healing.
To get rid of an abscess on your gums, your dentist will perform a surgical drainage procedure. Depending on the severity of the abscess, they may have to perform a or pull any affected teeth (. They may prescribe antibiotics as well.
For internal abscesses, your healthcare provider may perform a needle aspiration. Depending on the location of the abscess, you’ll receive local or general anesthesia. Then, they’ll guide a needle into place using an ultrasound or CT scan. They’ll drain the abscess using the needle. They may make a small incision in your skin and insert a thin plastic tube called a drainage catheter. The catheter allows the abscess to drain into a bag. You may have to leave the bag in place for a week or more.
Prevention
How can I prevent an abscess?
You can prevent skin abscesses by keeping your skin clean and dry. Bacteria getting into minor wounds cause most skin abscesses. Other steps you can take to prevent skin abscesses include:
- frequently.
- Not sharing towels, razors or toothbrushes.
- Avoiding nicking your skin while shaving.
- Maintaining a healthy diet.
- Practicing good
Preventing internal abscesses can be more difficult. They are typically complications of other conditions.
Outlook / Prognosis
What is the outlook for an abscess?
Minor skin abscesses may clear up on their own. But you should see your healthcare provider for any abscess that doesn’t go away within a couple of weeks. With treatment, the abscess will have the opportunity to drain properly and clear up. If you don’t get a skin abscess drained, it can continue to grow and fill with pus until it bursts. A burst abscess can be very painful and cause the infection to spread.
Treatment for tooth and other mouth abscesses is especially important. Untreated tooth abscesses can kill you. Untreated infections can spread to surrounding tissues in your body. This can cause serious complications including and necrotizing fasciitis, which can lead to death.
The outlook for internal abscesses depends on the location and treatment.
Additional Common Questions
What’s the difference between an abscess and a boil?
A boil (furuncle) is an abscess that forms at the site of a sweat gland or hair follicle and affects the surrounding tissue. Boils are smaller and closer to the surface of the skin than typical skin abscesses. Boils are commonly found on your neck, chest, face and buttocks. Boils are particularly painful in sensitive areas including your nose, ears and fingers.